What lurks in your mouth, very closeup
Categories: Health and Medicine | Microworld
By Pictolic https://pictolic.com/article/what-lurks-in-your-mouth-very-closeup.htmlWhat you will see in these photos, like rare plants or exotic landscapes, but in fact it is... bacteria that is nestled on your teeth, as well as other microorganisms living on the gums or on the toothbrush.
These macro photography were made with a microscope that scans a sample by a focused beam of electrons. After that the images were painted digitally or manually, to be able to distinguish individual elements. These photos belong to the Scientific photo lab in London and are used for research and educational purposes. They demonstrate to us the consequences of improper oral hygiene.
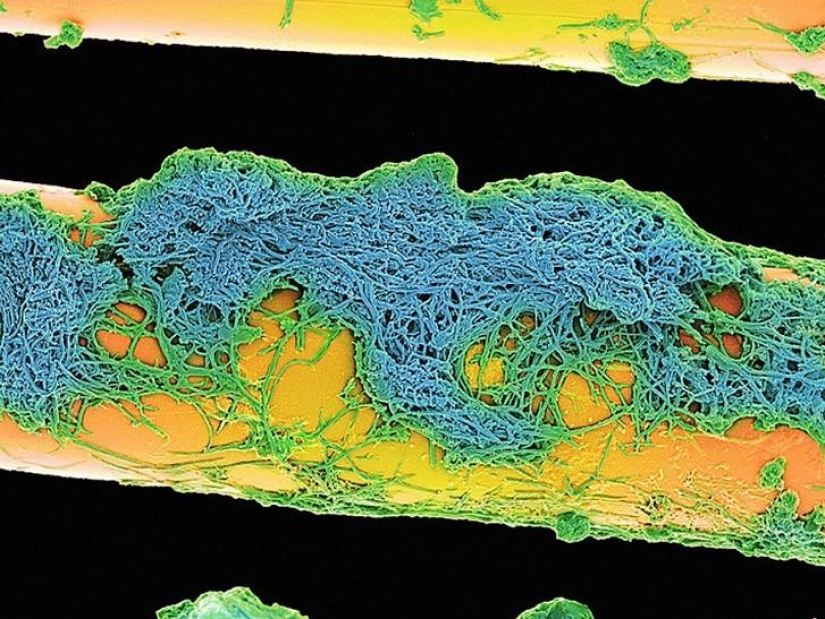
(SPL / Barcroft Media)
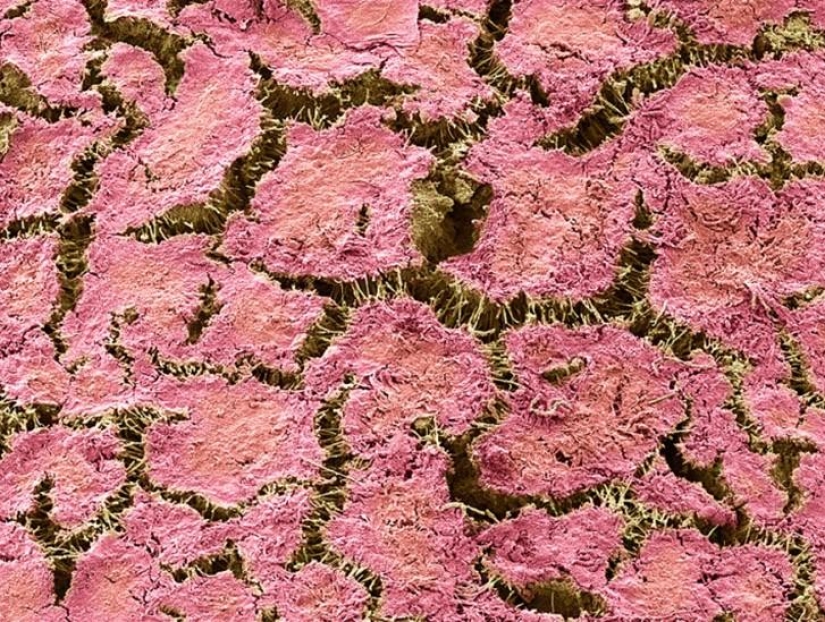
Plaque (magnification of 400 times, the width of the pattern 10 cm) — is a biofilm formed by colonizing bacteria trying to adhere to the tooth surface. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
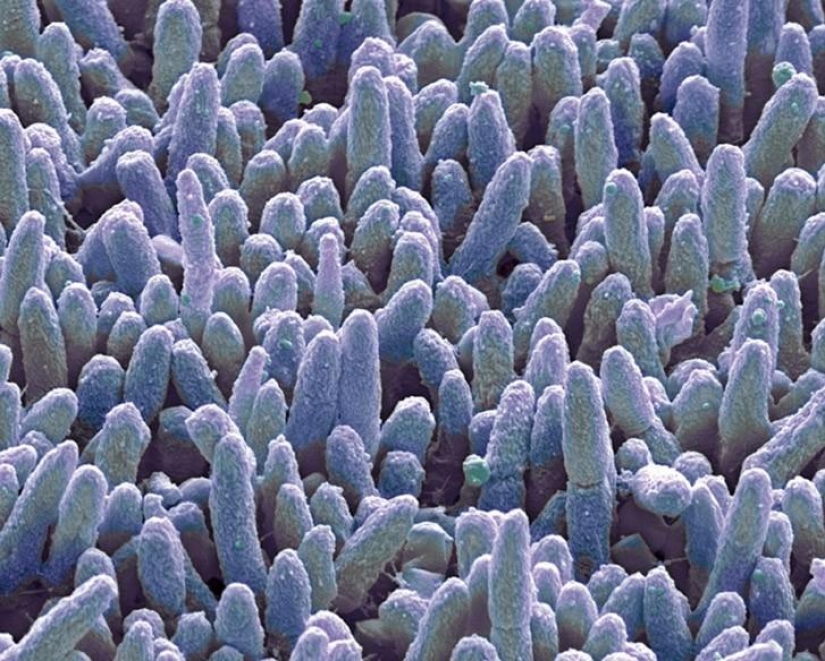
And this is the same plaque at a magnification of 10,000 times. Width remained unchanged. (SPL / Barcroft Media)

Milk the tooth. A large part of the human teeth made of dentin, a substance enveloping a cavity in which the soft connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves. Then the tooth crown covers the enamel (pictured above in white) — stronger and more mineralized substance that protects the dentin from acids in the mouth. At the root of the tooth, the dentin is protected by a substance called cement (pink), which serves as the means by which the periodontal ligaments can adhere to the tooth for stability. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
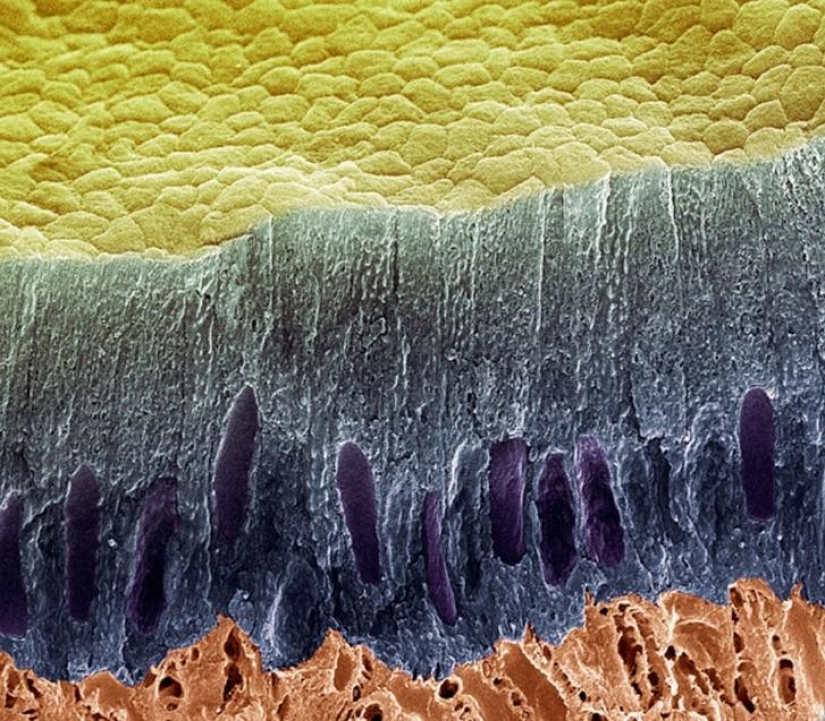
Shown here ameliorate layer of cells (blue), the surface of the tooth (yellow) and dentin (red). Loss of enamel or cement exposes the dentin — a porous substance with microscopic channels, called dentinal tubules that connect the pulp, leading to tooth sensitivity. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
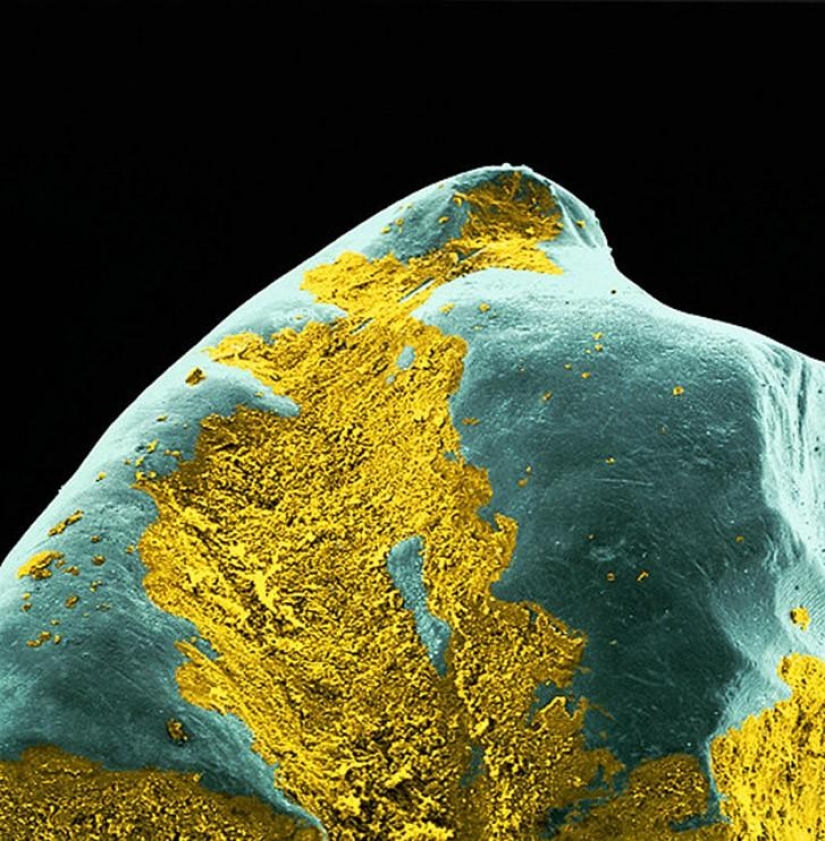
The yellow plaque on tooth surface. Acid is a waste formed during the digestive process of the bacteria. She demineralize the tooth, creating cavities that must be filled or which can lead to tooth loss. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
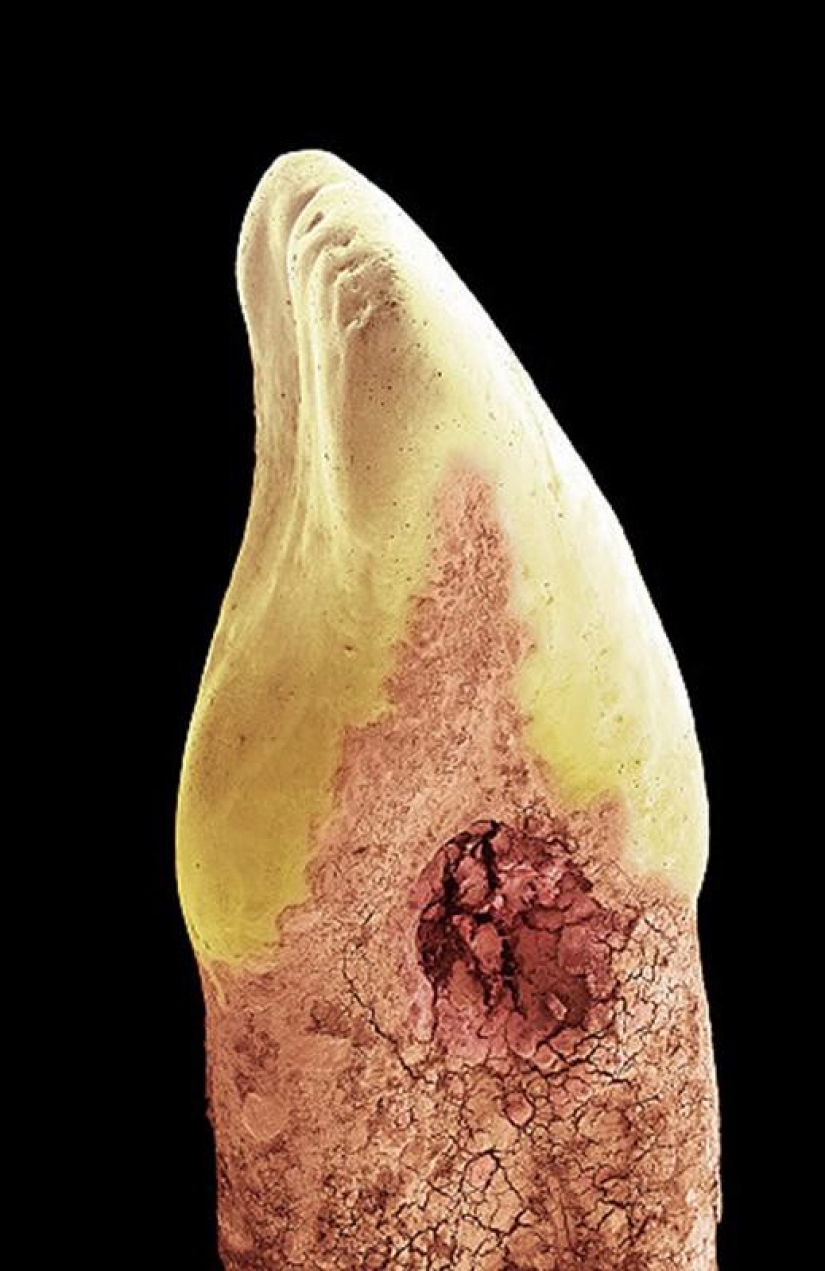
Human incisor with a cavity or the loss of minerals caused by bacterial acid "garbage". In this case, the cavities formed on the side of the tooth (between two teeth) and the gum-line (between the crown — yellow — and the root), perhaps due to lack of brushing flossing or from its improper use. British researchers found that one in three adults are prone to caries, and the study conducted on 5-year-old children in 2012, showed that every 4-th of them has a different degree of caries. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
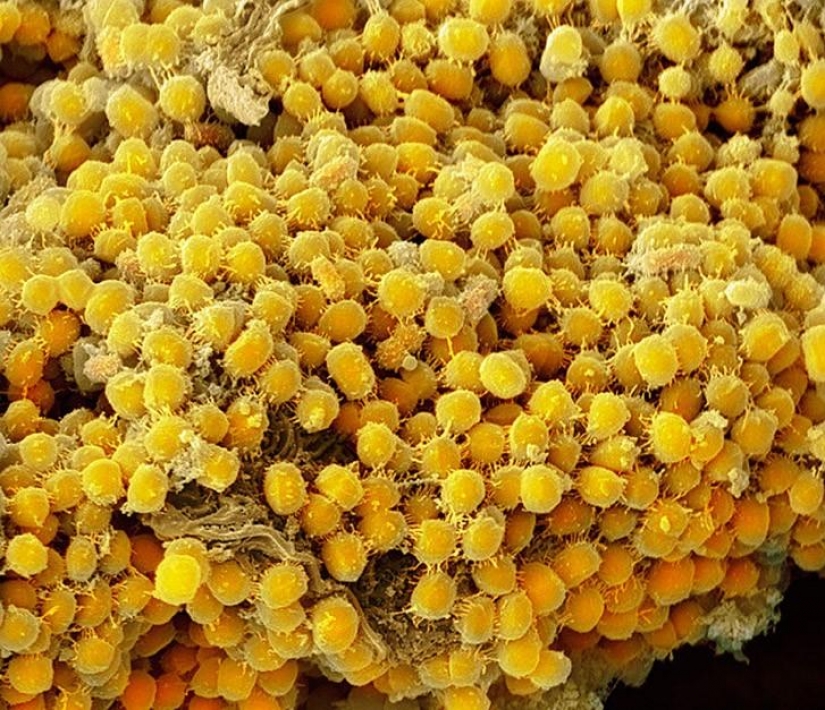

I hope this picture will convince you to floss every day... Yellow is the bacteria on the gums. Plaque buildup can lead to gum diseases such as gingivitis or periodontitis. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
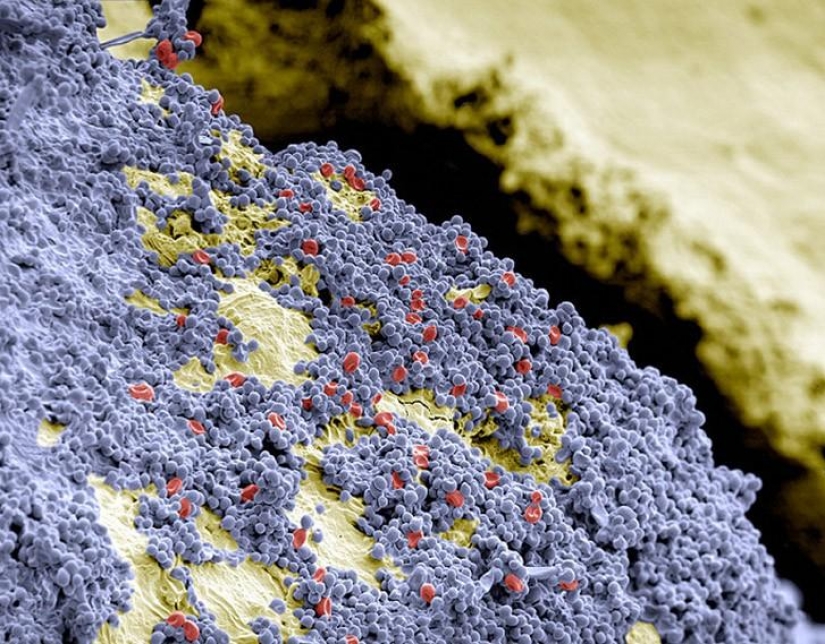
The surface of human tooth (colored yellow), a carpet of spherical bacteria (colored blue) and blood vessels (colored red). (SPL / Barcroft Media)
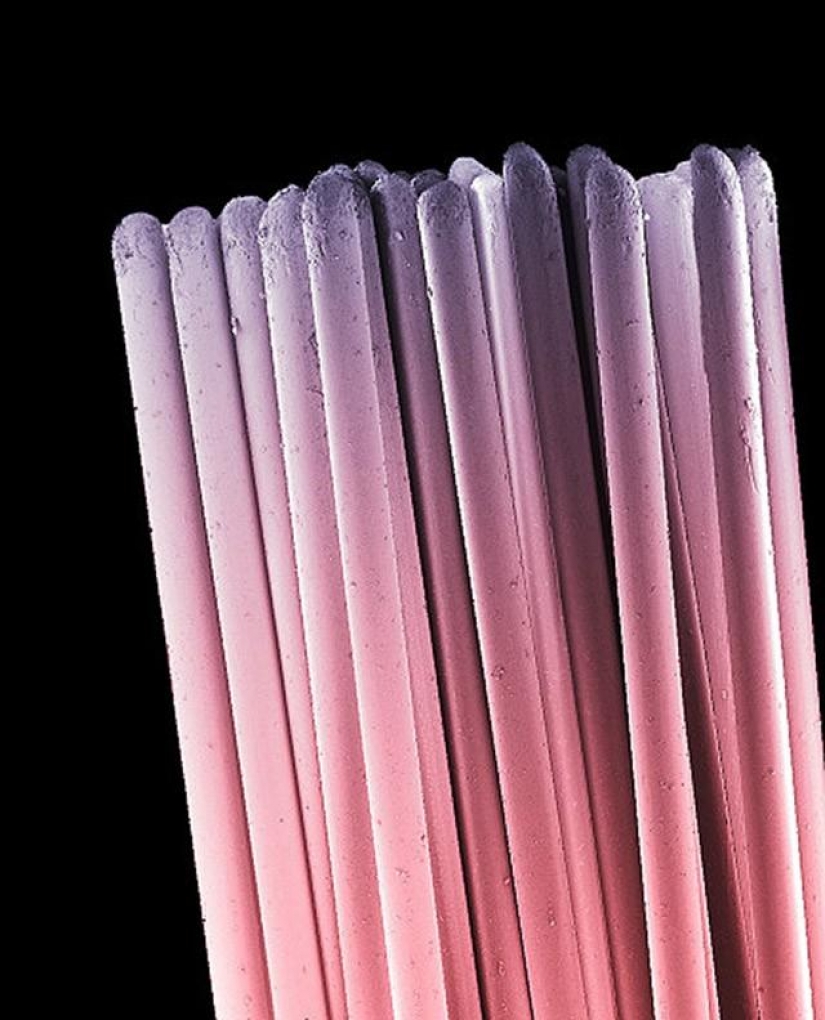

Toothbrush bristles. They fade and wear out over time, reducing the effectiveness of the toothbrush. Change your toothbrush is necessary at least every 3-4 months. However, wear can vary in different people depending on their habits to brush your teeth. If necessary, a toothbrush should be changed sooner. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
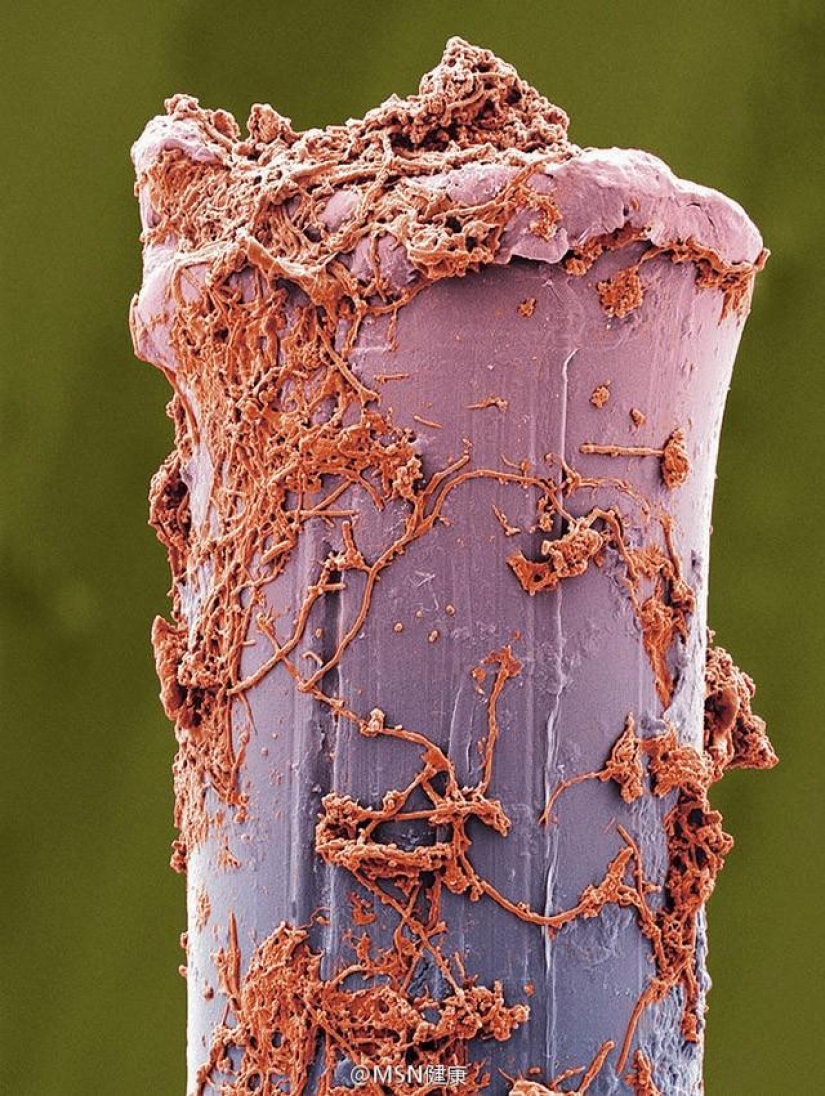
Toothbrush bristles covered with plaque. After brushing, the toothbrush should be thoroughly washed to remove all toothpaste residue or particles plaque and bacteria. It should dry in a standing position outdoors. In closed containers more moisture which promotes the growth of microorganisms. (SPL / Barcroft Media)

Dental plaque on the bristles used toothbrush at a magnification of 750 times. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
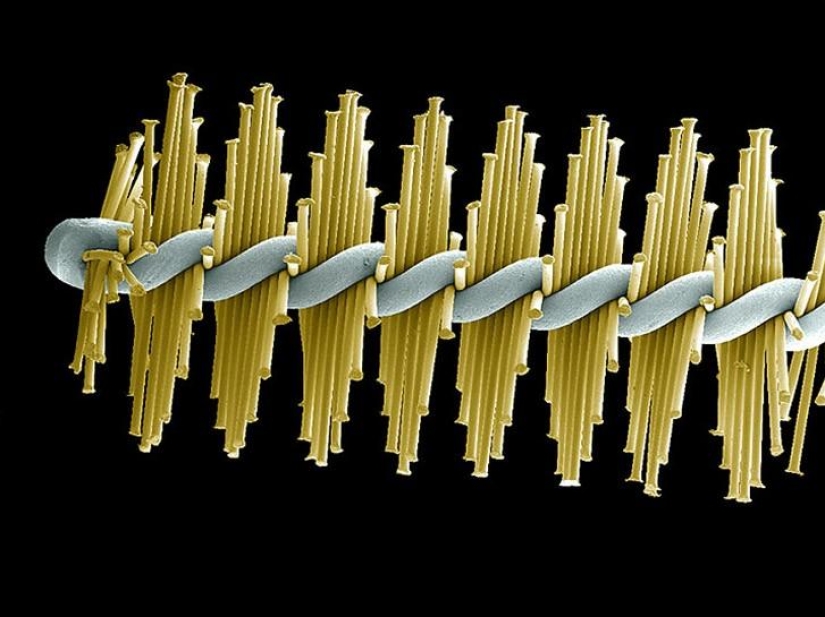

Interdental brushes (as pictured) have a small head with bristles designed for cleaning between your teeth. Your dentist may advise you to use interdental brush, but it does not replace floss. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
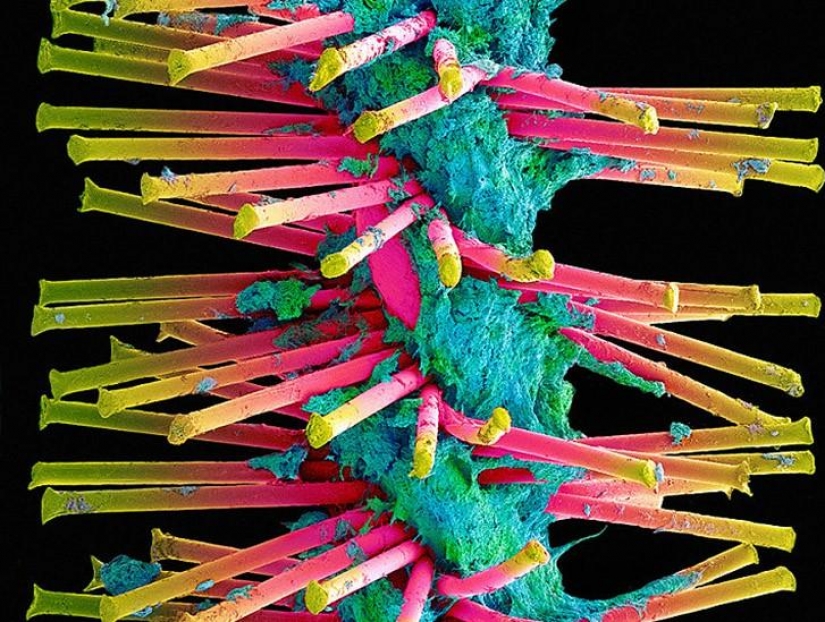
A more detailed view of the bristles used interdental brush covered in plaque. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
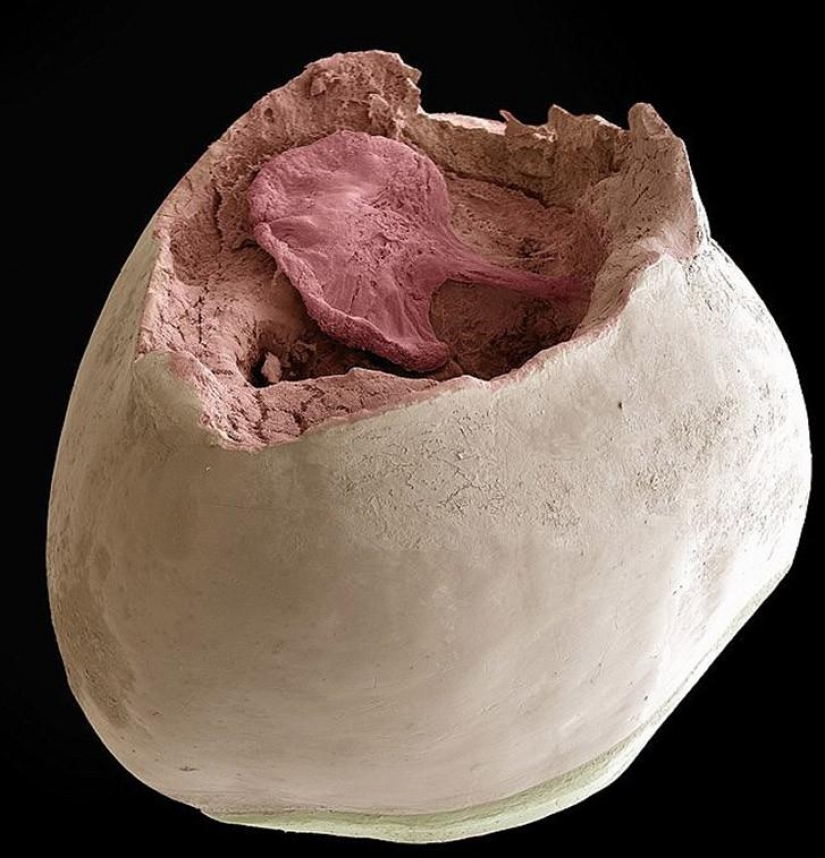
The milk tooth crown. Its root is stratified as a result of the process known as a temporary resorption of the tooth. This was due to pressure from the growing permanent tooth. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
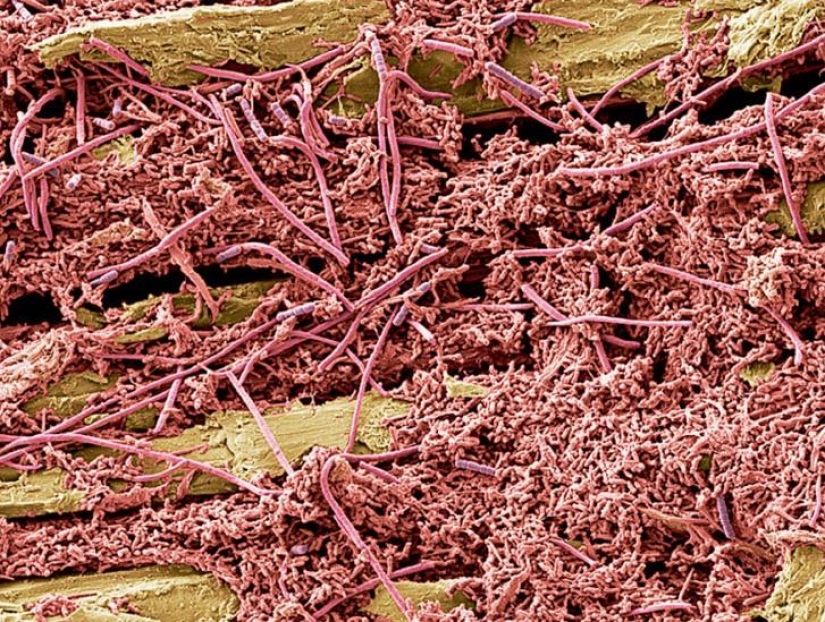
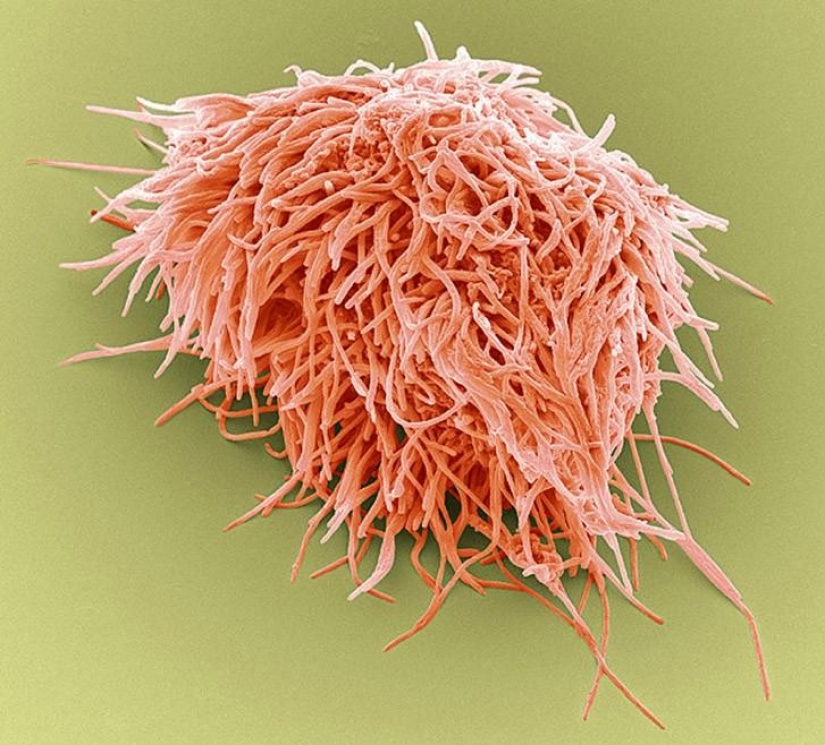
Narutoepisode bacteria at a magnification of 1000 times. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
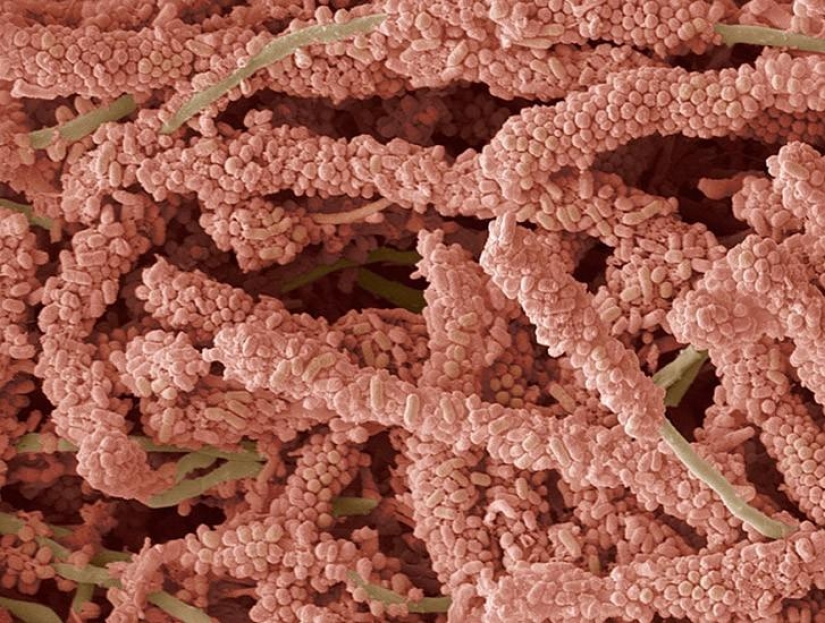
The bacteria that form plaque. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
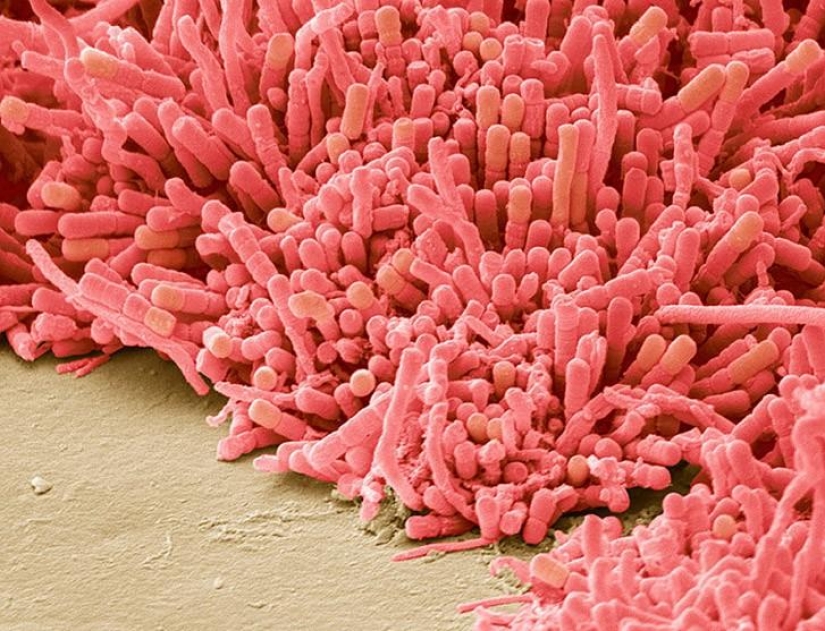
The bacteria that form plaque, at a magnification of 8000 times. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
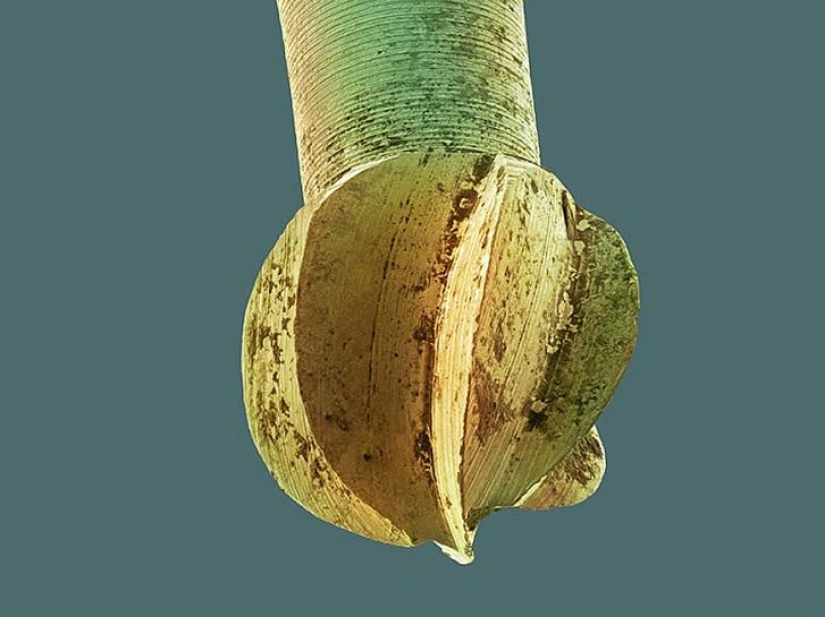

Among other applications, a drill (pictured) is also used to remove soft tissue and bacteria from plaque before preparing the filling, otherwise the filling can begin to form new plaque. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
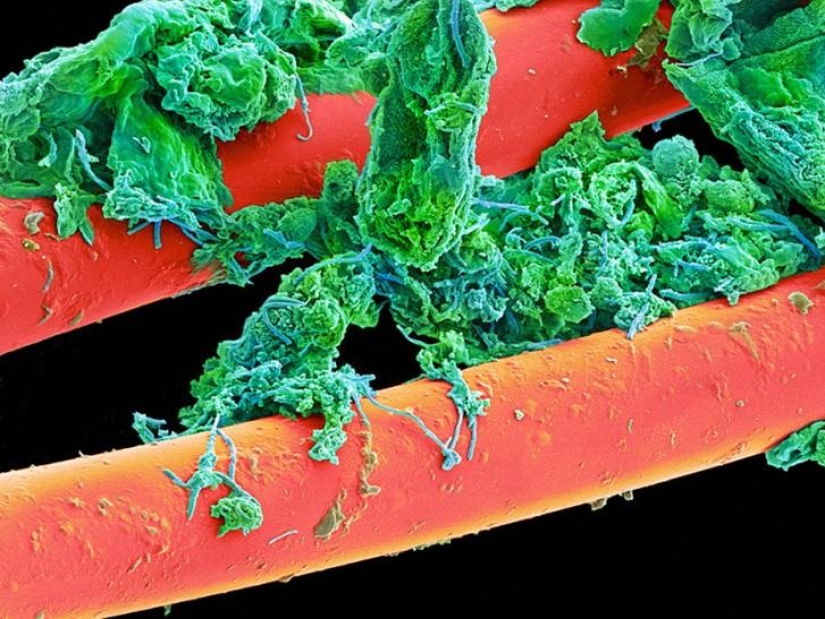
This is the tip of the drill. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
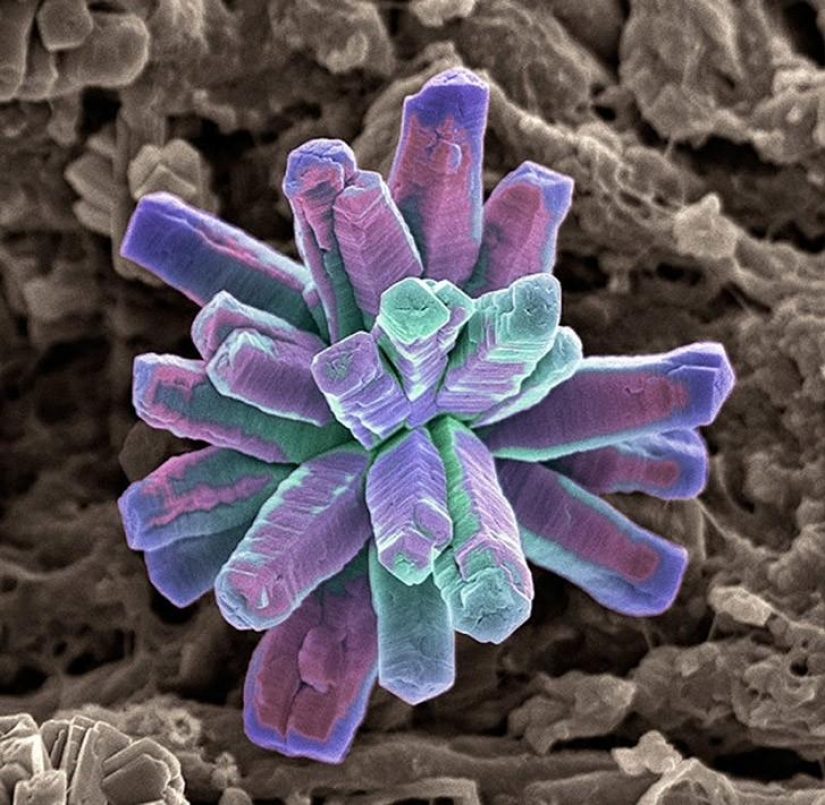
Crystals of calcium phosphate used for remineralization of the tooth after the loss of minerals by bacteria. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
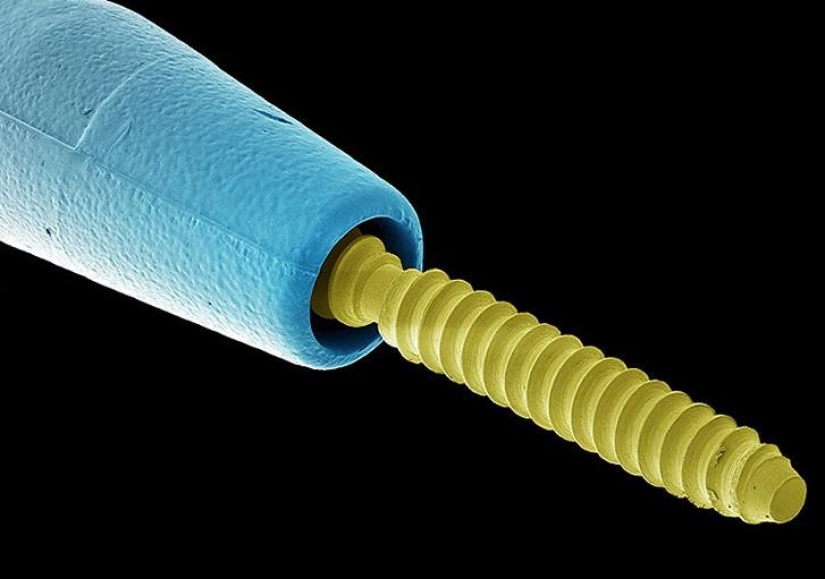
Dental posts to strengthen the material for fillings and crowns when a large part of the tooth disintegrated or missing. (SPL / Barcroft Media)
Keywords: Bacteria | Teeth | Macro | Mouth
Post News ArticleRecent articles

It's high time to admit that this whole hipster idea has gone too far. The concept has become so popular that even restaurants have ...

There is a perception that people only use 10% of their brain potential. But the heroes of our review, apparently, found a way to ...
Related articles

"Wash your hands before eating!" — a phrase familiar to us since childhood. The parents explained that with the help of this ...

If you avoid dentists, do not go to preventive examinations, and appear at the reception when the toothache is absolutely ...

A startlingly beautiful earth snail crawled up the back of a crested crocodile and looked right into its toothy mouth. The unusual ...

New Year's is a time to surprise and delight loved ones not only with gifts but also with a unique presentation of the holiday ...