Brighter than a thousand suns: 20 scary shots in memory of the nuclear explosion in Hiroshima
Categories: History
By Pictolic https://pictolic.com/article/brighter-than-a-thousand-suns-20-scary-shots-in-memory-of-the-nuclear-explosion-in-hiroshima.htmlOn August 6, 1945, the United States dropped an atomic bomb on the Japanese city of Hiroshima, using nuclear weapons for the first time in history. There is still a debate about whether this action was justified, because Japan was close to capitulation at that time. Anyway, on August 6, 1945, a new era in the history of mankind began.
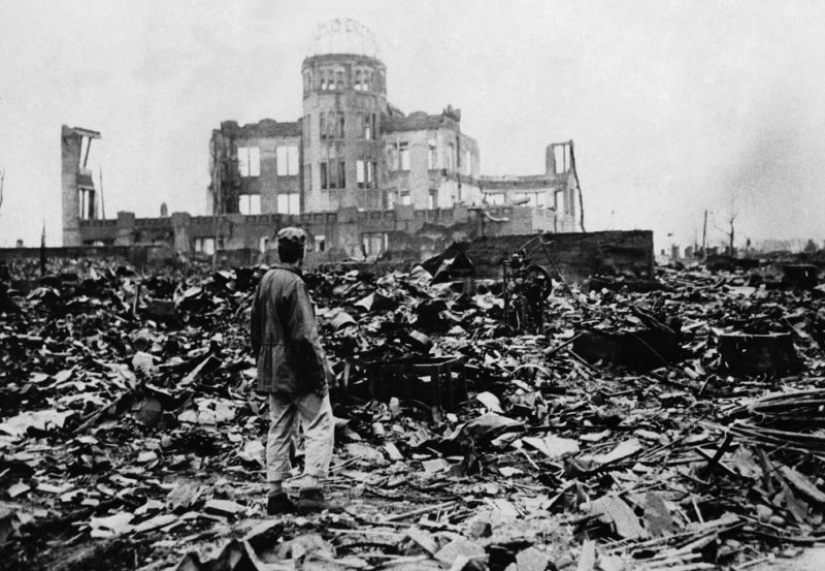
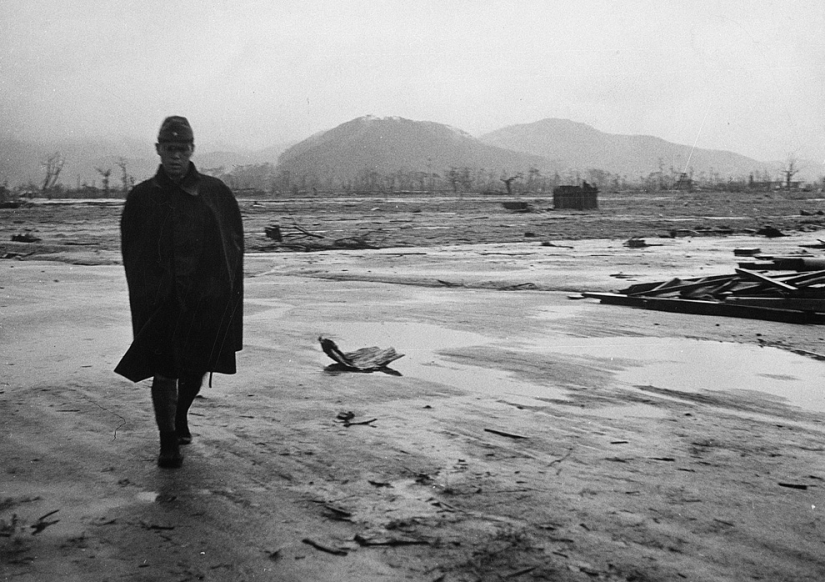


A Japanese soldier walks through a deserted area in Hiroshima in September 1945, just a month after the bombing. This series of photographs depicting the suffering of people and ruins was presented by the US Navy. (U.S. Department of Navy)

Aerial view of Hiroshima shortly before the bomb was dropped on the city in August 1945. It shows a densely populated area of the city on the Motoyasu River. (Hiroshima: The United States Strategic Bombing Survey Archive, International Center of Photography, Purchase, with funds provided by the ICP Acquisitions Committee, 2006)

Data of the US Air Force-a map of Hiroshima before the bombing, on which you can observe the area of the epicenter, which instantly disappeared from the face of the earth. (U.S. National Archives and Records Administration)
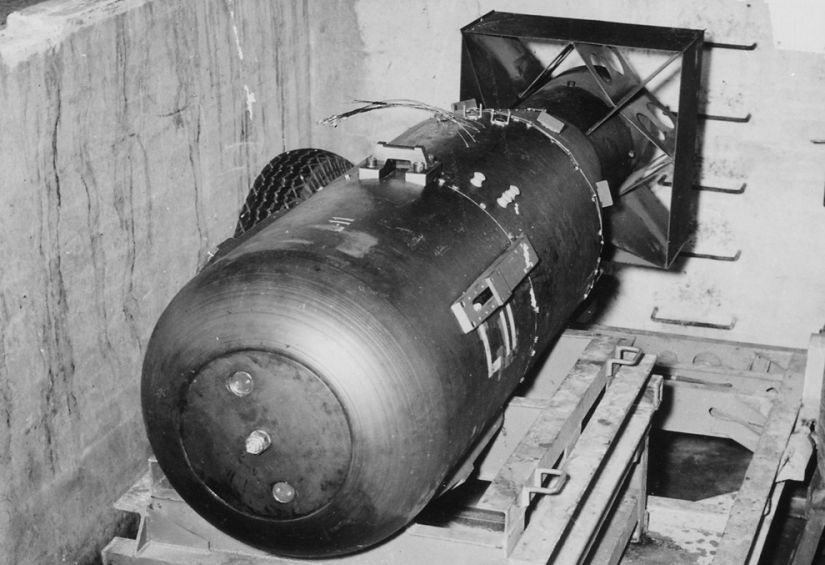
A bomb codenamed "Kid" over the airlock of a B‑29 Superfortress "Enola Gay" bomber at the base of the 509th Composite Group in the Mariana Islands in 1945. The "baby" was 3 m long and weighed 4000 kg, but contained only 64 kg of uranium, which was used to provoke a chain of atomic reactions and the subsequent explosion. (U.S. National Archives)
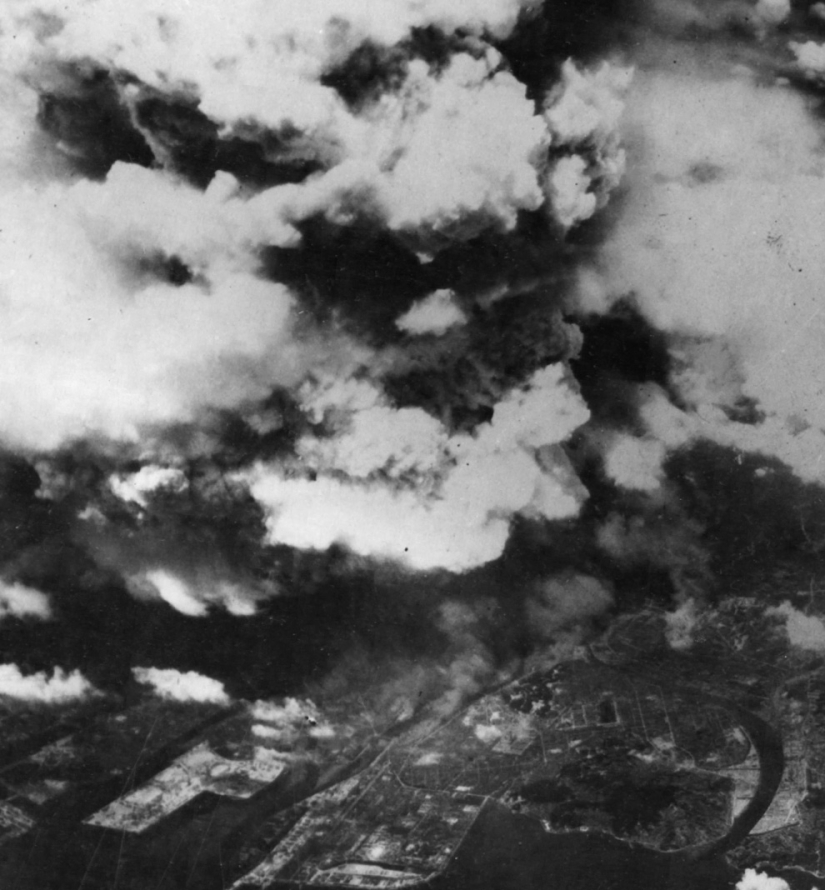

A photo taken from one of the two American bombers of the 509th Composite Group, shortly after 8: 15, on August 5, 1945, shows smoke rising from the explosion over the city of Hiroshima. By the time of the shooting, there was already a flash of light and heat from a fireball with a diameter of 370 m, and the blast wave was quickly dissipating, having already caused the main damage to buildings and people within a radius of 3.2 km. (U.S. National Archives)

A growing nuclear "mushroom" over Hiroshima shortly after 8: 15, August 5, 1945. When the portion of uranium in the bomb passed the stage of splitting, it instantly turned into the energy of 15 kilotons of TNT, heating the massive fireball to a temperature of 3980 degrees Celsius. The air, heated to the limit, quickly rose in the atmosphere like a huge bubble, raising a column of smoke behind it. By the time this photo was taken, the smog had risen to a height of 6096 m above Hiroshima, and the smoke from the explosion of the first atomic bomb scattered to 3048 m at the base of the column. (U.S. National Archives)
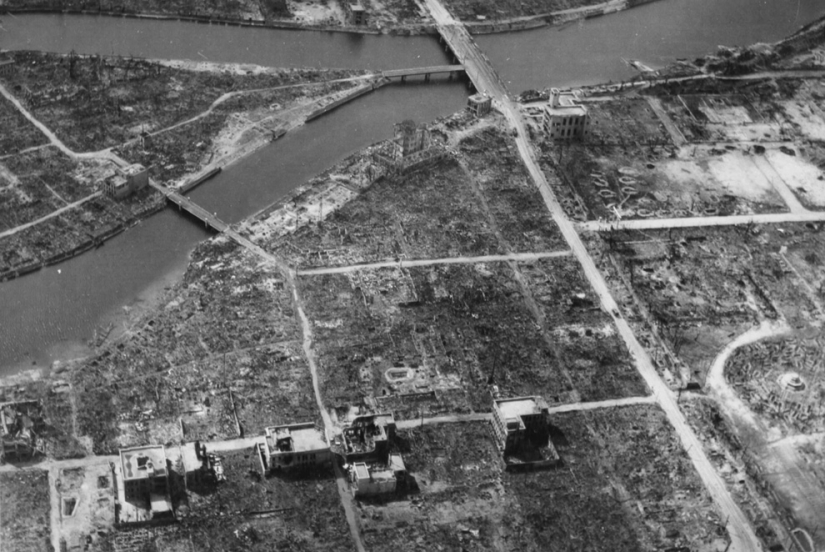

View of the epicenter of Hiroshima in the fall of 1945 — complete destruction after the first atomic bomb was dropped. The photo shows the hypocenter (the central point of the explosion center) - approximately above the Y-shaped intersection in the center on the left. (U.S. National Archives)
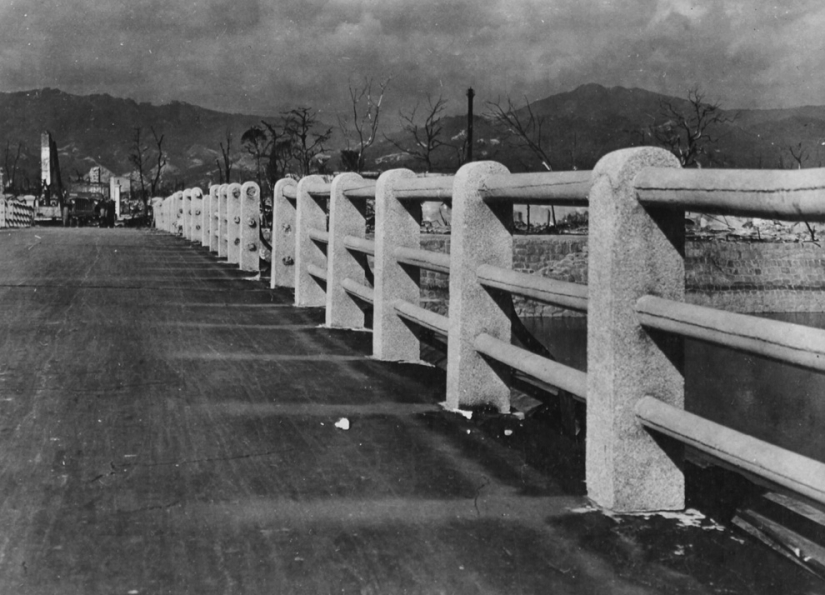

The bridge over the Ota River is 880 meters from the hypocenter of the explosion over Hiroshima. Notice how the road burned down, and on the left you can see ghostly prints where once the surface was protected by concrete columns. (U.S. National Archives)
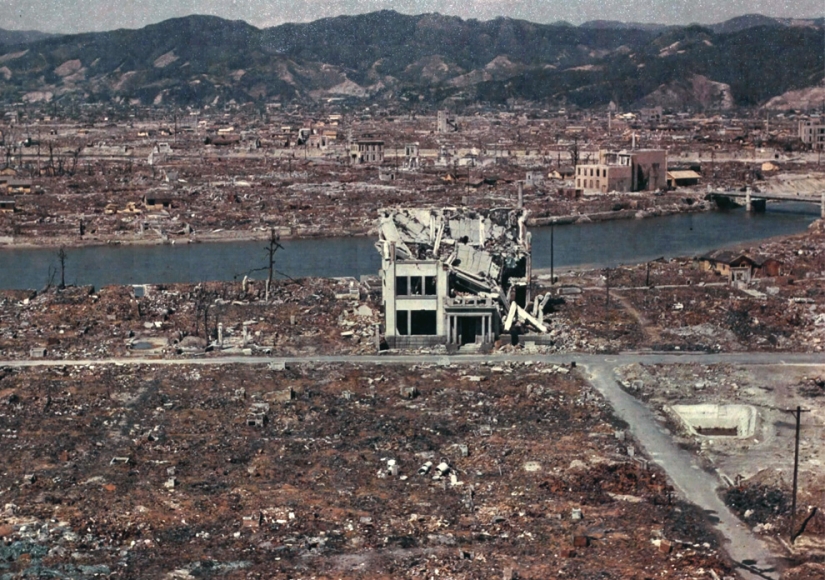

Color photo of the destroyed Hiroshima in March 1946. (U.S. National Archives)
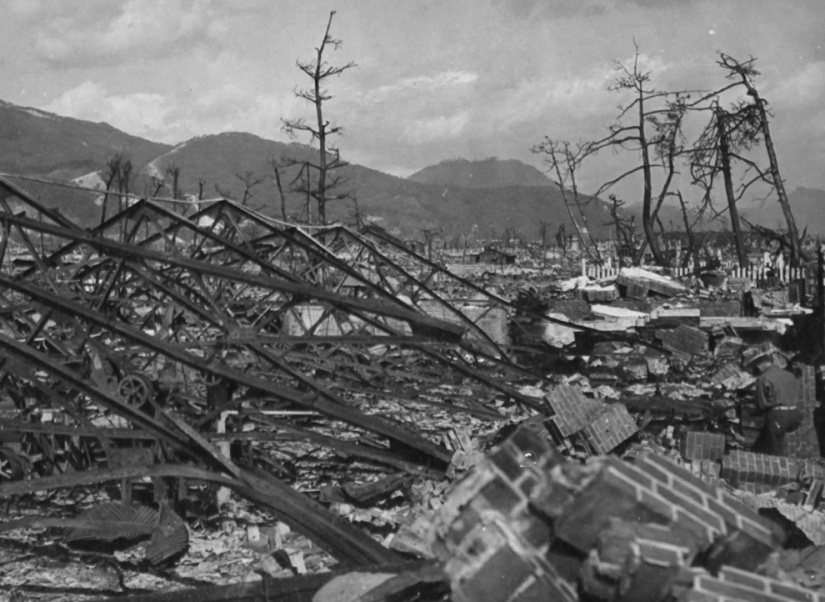

An explosion destroyed the Okita plant in Hiroshima, Japan. November 7, 1945. (U.S. National Archives)
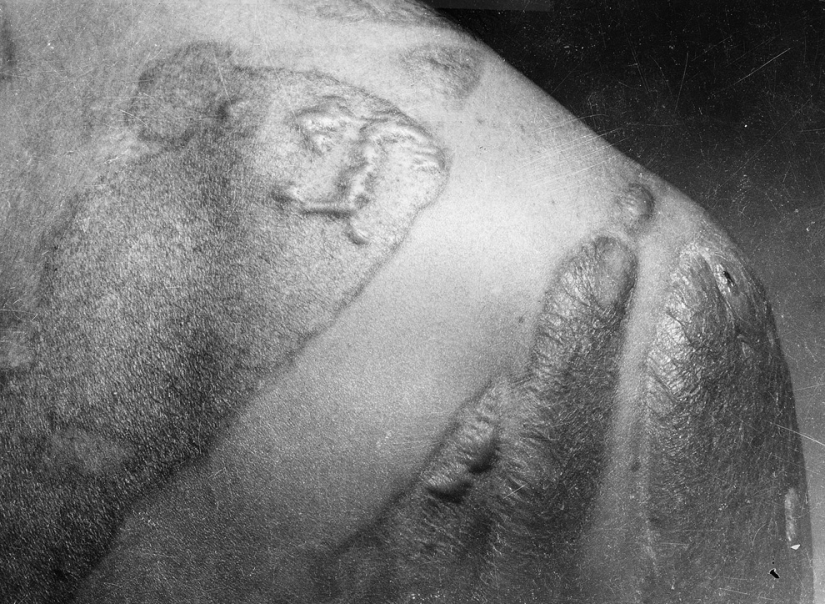
Keloid scars on the back and shoulders of the victim of the explosion in Hiroshima. The scars were formed where the victim's skin was not protected from direct radiation rays. (U.S. National Archives)
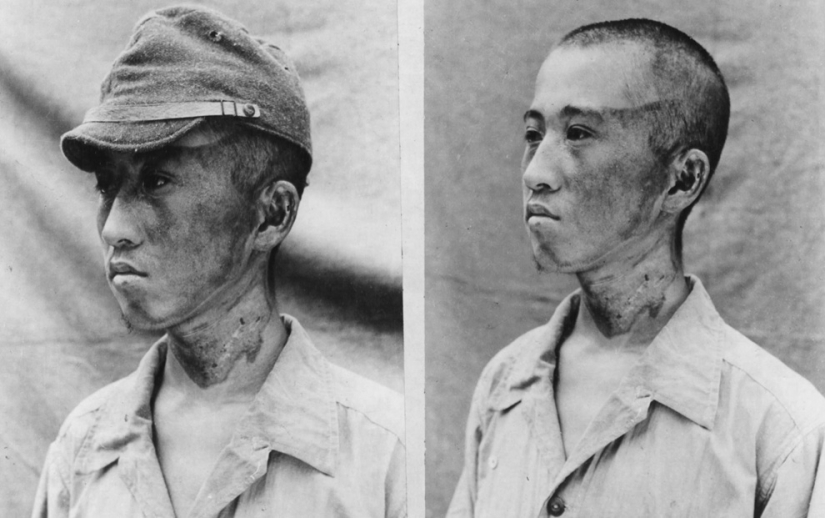
This patient (the picture was taken by the Japanese military on October 3, 1945) was about 1981.2 m from the epicenter when radiation rays overtook him on the left. The cap protected part of the head from burns. (U.S. National Archives)
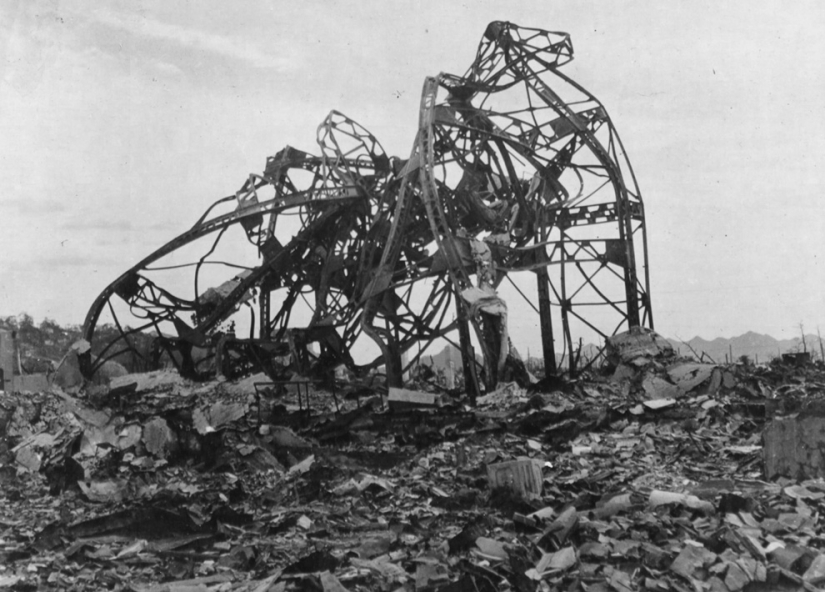

Twisted iron crossbars are all that remains of the theater building, which was located about 800 meters from the epicenter. (U.S. National Archives)
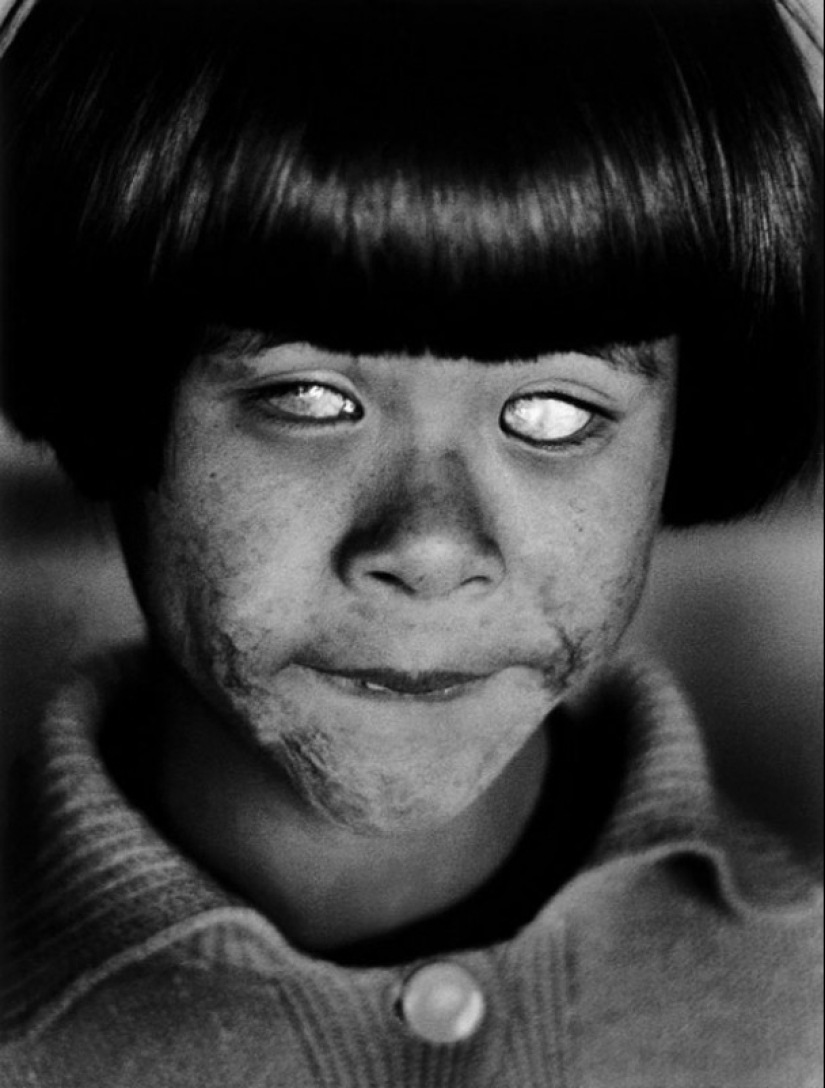
A girl who went blind after a nuclear explosion.

Color photo of the ruins of Central Hiroshima in the fall of 1945. (U.S. National Archives)
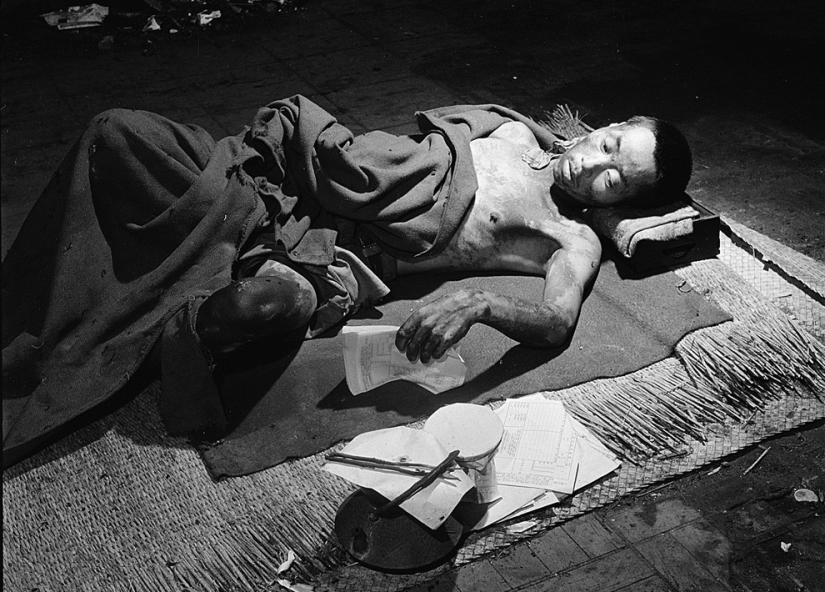

A victim of the bombing in Hiroshima lies in a temporary hospital located in one of the surviving bank buildings in September 1945. (U.S. Department of Navy)
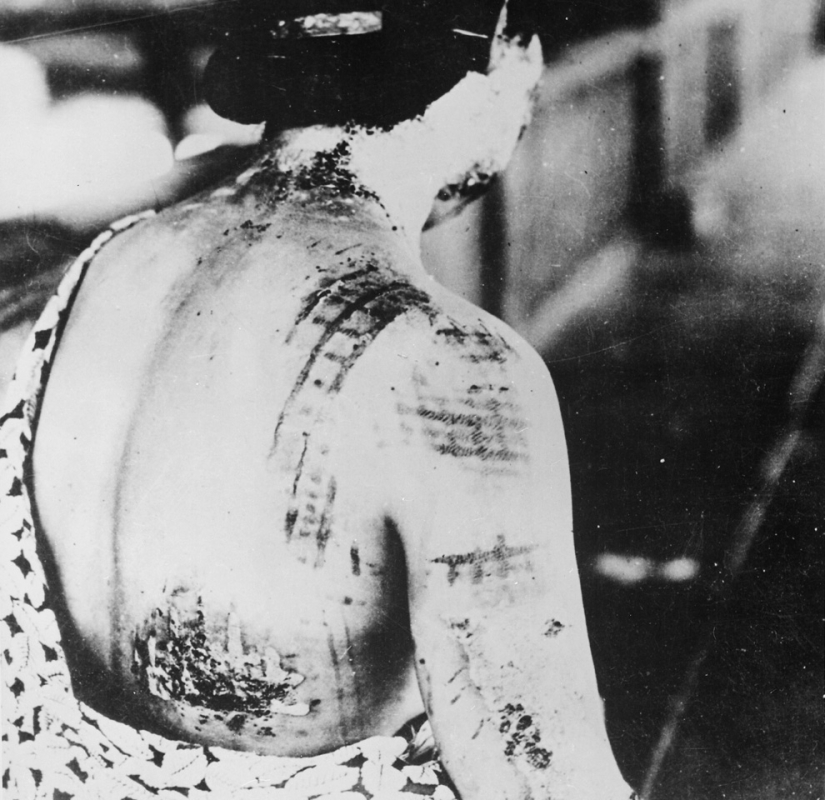
From the photo caption: "The burns on the patient's skin were left in the form of dark spots from the kimono that the victim was wearing at the time of the explosion." (U.S. National Archives)
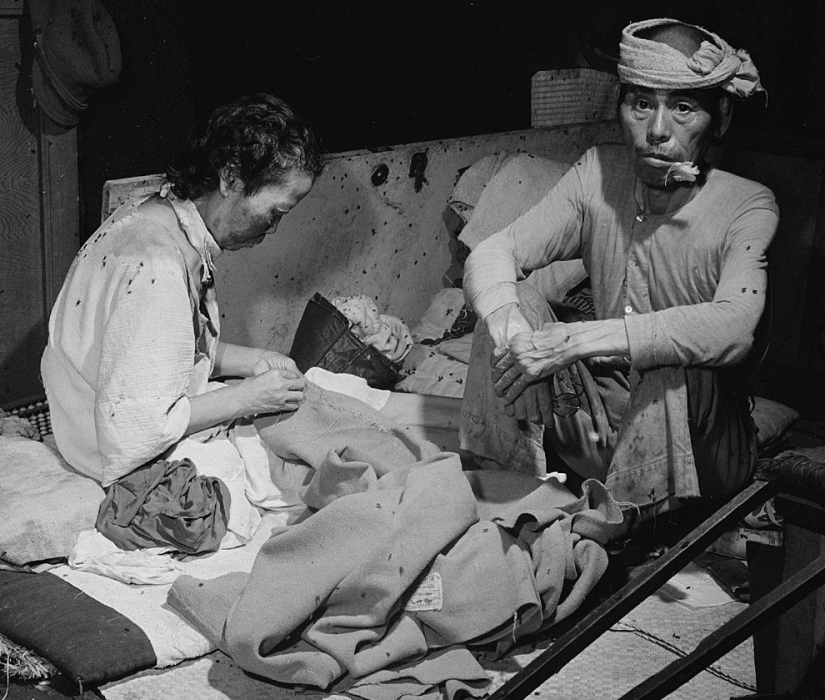
Victims of an explosion in a fly-infested temporary hospital in a bank building in Hiroshima on September 15, 1945. (U.S. Department of Navy)
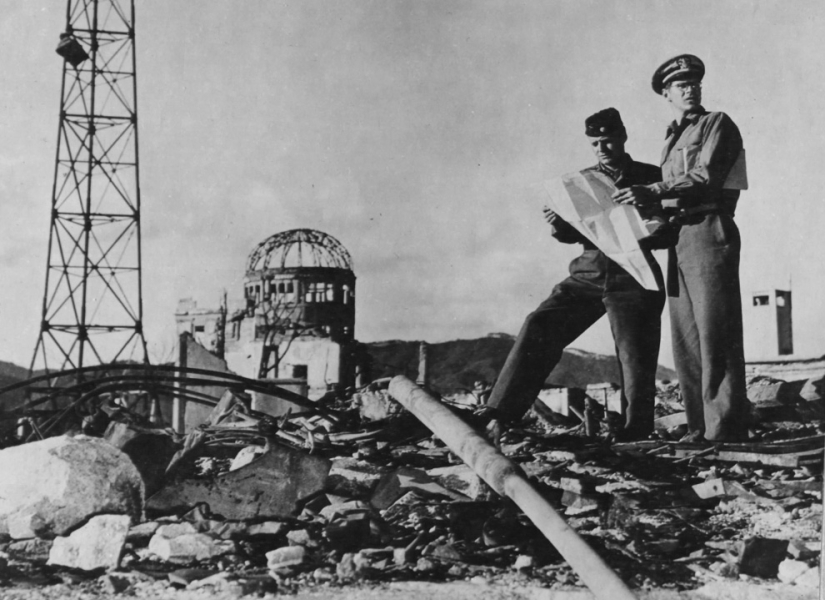

The US military explores the area around the epicenter in Hiroshima in the fall of 1945. (U.S. National Archives)
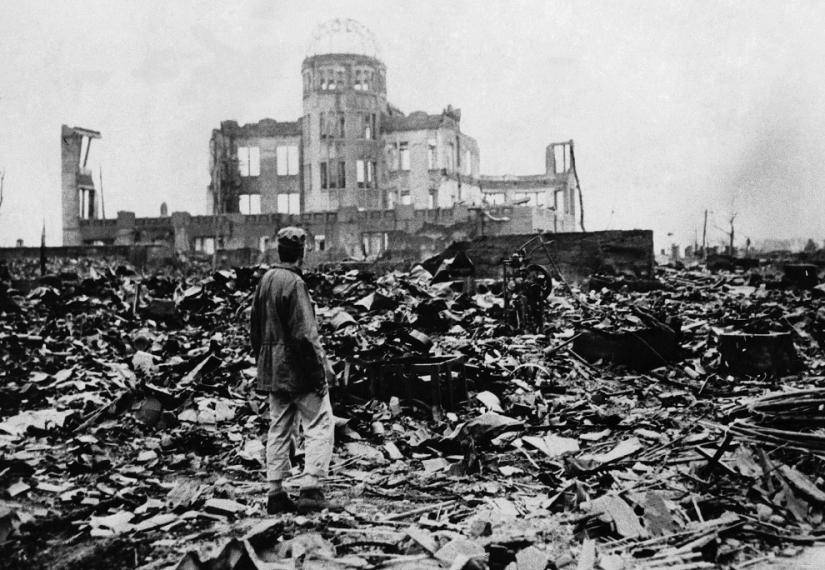

Unknown person on the ruins in Hiroshima. (AP Photo)
Keywords: USA | Japan | History | Museum | Nuclear weapons | Bomb | Hiroshima
Post News ArticleRecent articles

It's high time to admit that this whole hipster idea has gone too far. The concept has become so popular that even restaurants have ...

There is a perception that people only use 10% of their brain potential. But the heroes of our review, apparently, found a way to ...
Related articles

In the fall of 1972, Bill Yates traveled through the countryside in the vicinity of Tampa, Florida. At that time, he was studying ...

When a person is in a life-threatening situation is awful, but even worse when it happens to a child. 11-year-old American Terry ...

Remember how broke the "unbreakable" scoop? The photo preserved in the photo album of almost every family! A selection of vintage ...

New Year's is a time to surprise and delight loved ones not only with gifts but also with a unique presentation of the holiday ...