What the 9 Most Popular Harmful Substances, including Alcohol, LSD and Caffeine, Do to Your Brain
Categories: Health and Medicine
By Pictolic https://pictolic.com/article/what-the-9-most-popular-harmful-substances-including-alcohol-lsd-and-caffeine-do-to-your-brain.htmlSniff — and the world turns into a colorful kaleidoscope of dancing patterns and waves of sounds; take a sip — and the muscles in your body spread like jelly. Yes, different substances allow a person to explore the world around in completely different ways, but their consequences can not be called pleasant in any way. So what do narcotic substances actually do to the human brain? Let's find out.
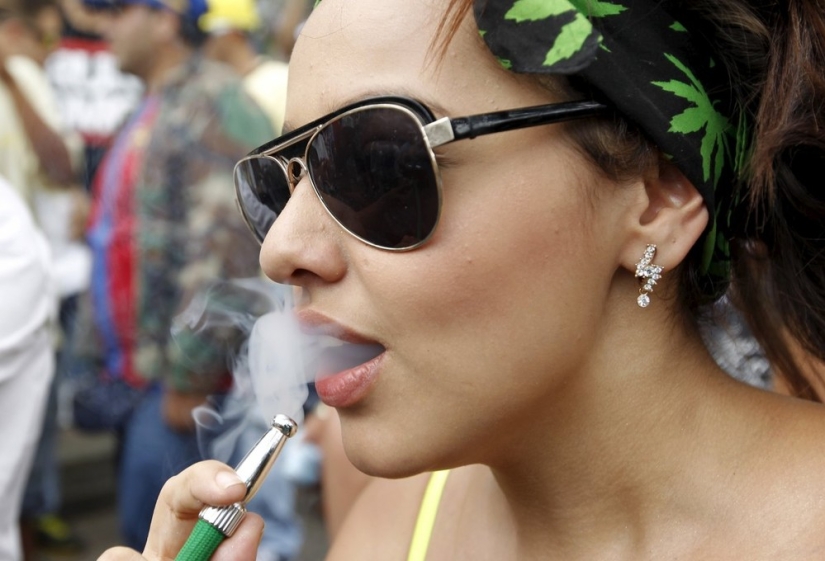


When the active substance of marijuana — tetrahydrocannabinol — enters the brain, it prompts its cells to secrete the "pleasant" neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine is part of the brain's reinforcement system, it makes us feel good and get maximum enjoyment from simple things like food or sex. Overexcited, the reinforcing system creates a feeling of euphoria. That is why, in some rare cases, excessive use of marijuana can become a problem: the more often a person enters a state of euphoria, the less other feelings he experiences.
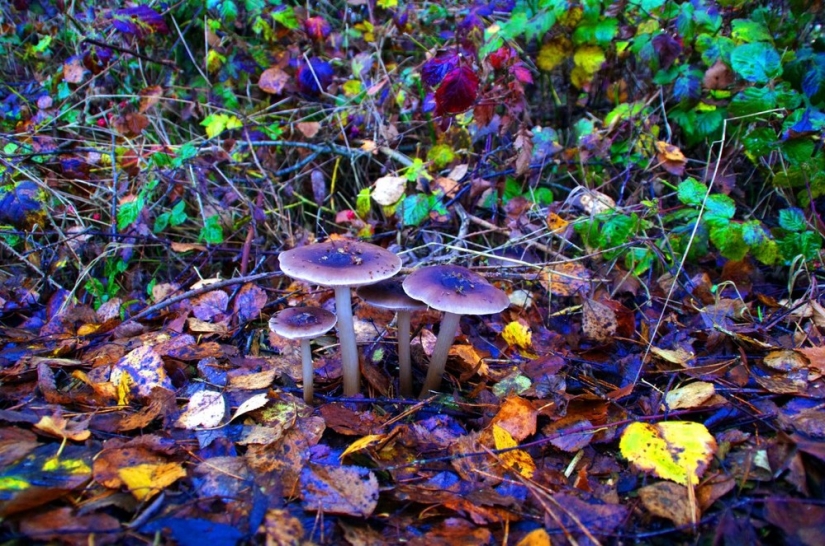

A recent study showed that the main psychotropic ingredient of mushrooms — psilocybin — suppresses normal brain activity and instead jerkily triggers new connections between its various areas. Perhaps it is these new connections that cause hallucinations like "I see sounds" or "I hear colors" and give mushrooms the effect of an antidepressant. It should be borne in mind that eating mushrooms is associated with health risks, including unpleasant hallucinations and a growing sense of anxiety.
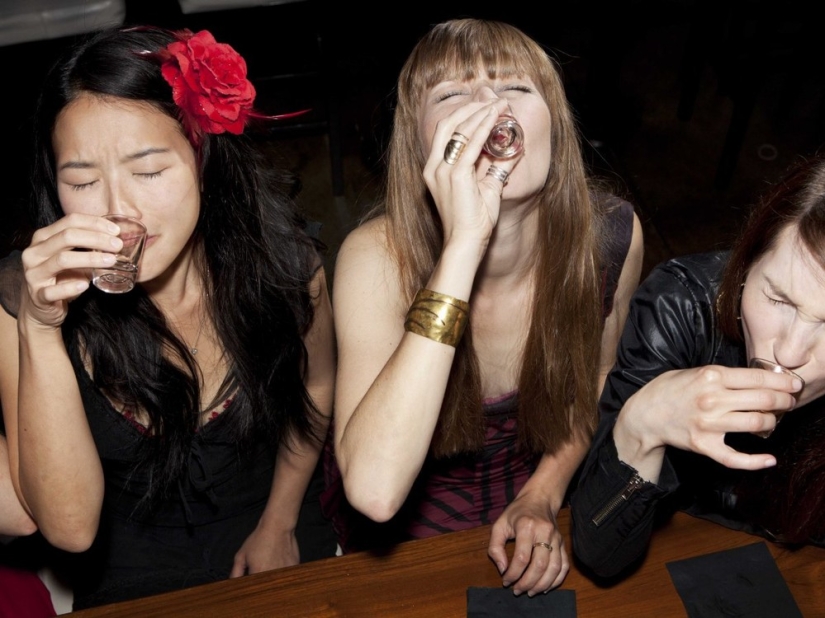

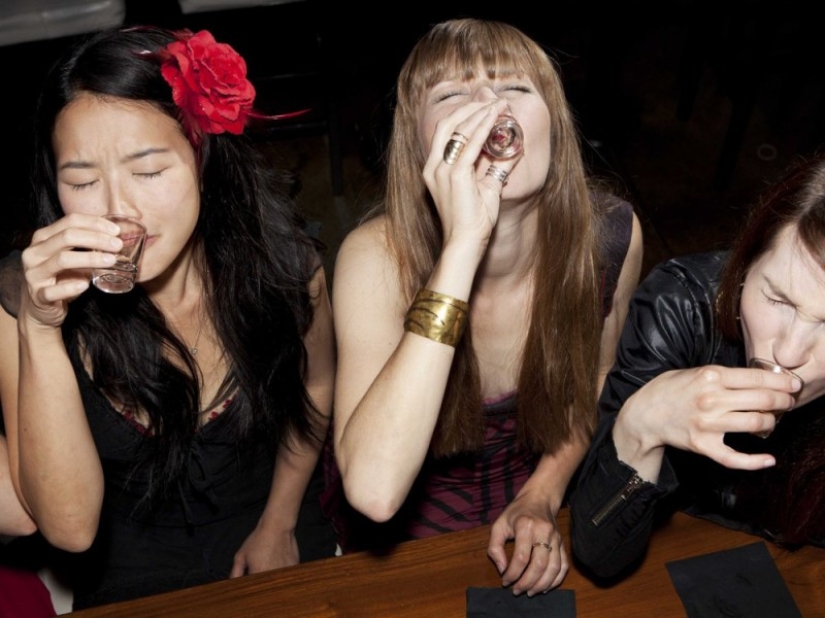
Like any other drug, alcohol affects brain chemistry by changing the levels of neurotransmitters —chemical transmitters that transmit signals that control our thinking and behavior. Alcohol slows down thinking, breathing and heartbeat, stopping our "excitatory" transmitters — those that usually increase energy levels. But it amplifies our "inhibitory" transmitters — those that usually make us calm down. That's why they say: drunk and the sea is knee-deep.
The brain transforms heroin into morphine, which binds to molecules in brain and body cells called opioid receptors. They affect the perception of pain and pleasant sensations. This explains the incredibly strong feeling of euphoria that many experience when administered this drug. Since opioid receptors are also found in the brain stem, the main control center, an overdose can lead to slowing or stopping breathing, brain damage, coma, or even death.
A recent study has shed light on the potential link between heroin and opioid painkillers such as vicodin or oxycontin. People who abused opiates were 40 times more likely to start using heroin. This is because the nature of the effect of opiates on the brain is similar to the effect of heroin.

Caffeine is the most common psychotropic substance in the world. It stimulates the central nervous system and temporarily lifts the mood. But it is also able to increase the level of adrenaline, which charges with energy and potential for active activity, but in the end it can provoke anxiety and irritability. In its structure, caffeine is similar to adenosine molecules, which, in turn, reduces the processes of excitation in the brain. Replacing it with caffeine leads to a stimulating effect.

Like magic mushrooms, LSD is a hallucinogen. Hallucinogens affect mainly the area of the brain responsible for regulating our mood, thoughts and perception, but also affect how we respond to stress. LSD causes a variety of hallucinations — for example, under its influence you can feel flying or see your own death from the outside. Short-term effects of LSD can include impulsivity, a rapid change of emotions from euphoria to sadness, dizziness and increased heartbeat.

Since flakka is a relatively new drug, the mechanism of its effect on the brain has not yet been thoroughly studied. At the moment, you can compare it with close "relatives" like cocaine or amphetamine. These drugs cause a rush of two substances: dopamine (a "good" neurotransmitter) and norepinephrine, which speeds up the heartbeat and increases the level of excitement. Like most other drugs, flakka has "waste products". Often this is expressed in the fact that a person returns to drug use again and again in order to get rid of negative feelings. Overdose is associated with side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations and aggressive behavior.

Ecstasy, or MDMA, excites the activity of at least three different neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin, which play a crucial role in maintaining a good mood. Elevated serotonin levels may explain the surge in mood and energy experienced by people who have taken MDMA, but a decrease in the level of the same serotonin is also the cause of long days of melancholy. Scientists have proven that chronic MDMA use (a couple of pills every weekend for several years or 10-20 tablets per weekend) has a very bad effect on brain function. People who take MDMA constantly lose their memory and the ability to clearly perceive information.
Recent articles

It's high time to admit that this whole hipster idea has gone too far. The concept has become so popular that even restaurants have ...

There is a perception that people only use 10% of their brain potential. But the heroes of our review, apparently, found a way to ...

New Year's is a time to surprise and delight loved ones not only with gifts but also with a unique presentation of the holiday ...