6 advanced technologies that are changing our lives today
Categories: Science | Technology
By Pictolic https://pictolic.com/article/6-advanced-technologies-that-are-changing-our-lives-today.htmlSince 2001, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has chosen leading technological achievements every year, which, according to its calculations, will have a tangible impact on each of us in the near future. Not all of the scientific discoveries that you will learn about below were made this year — some of them are already several decades old.
This is due to the fact that when compiling the list, experts paid attention not so much to a specific scientific breakthrough in a particular field, as to a whole range of factors that allow us to accurately state which technologies will really enter our lives. This is the maturity of the technology, and the existence of ready-made inventions based on it, as well as what tasks it solves — how significant it is and what areas of life it can affect. For example, 3D printing technology was first patented in 1989 by Immanuel Sachs, and only in 2017 his startup Desktop Metals launched the first batch of 3D printers for metal.
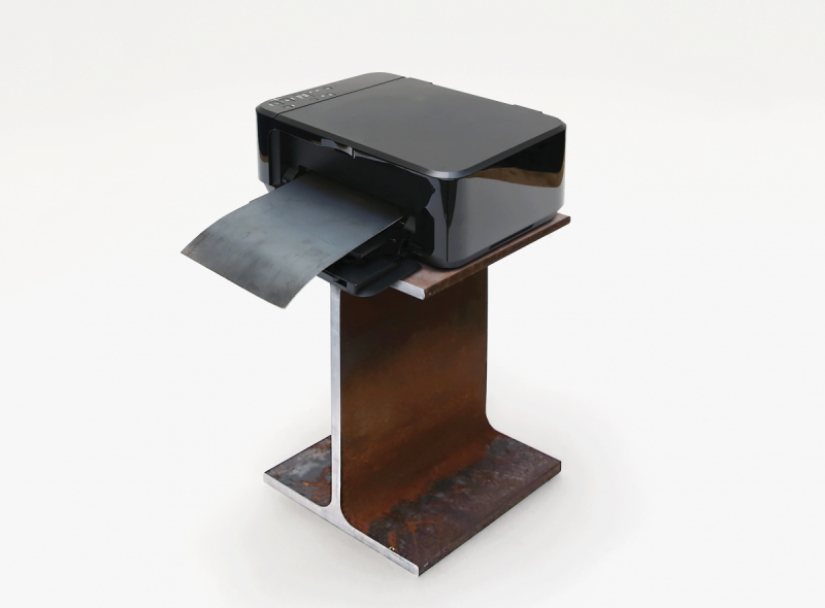


3D printing
3D printing has long remained the domain of individual designers and enthusiasts. However, the gradual improvement of the technology has made it possible to reduce the costs and price of printing so that today it is becoming increasingly popular and may soon radically change modern mass production.
Giant factories producing a narrow range of goods in large quantities will be replaced by smaller, producing a wide range of productions — because with the help of 3D printing, you can instantly and in the right amount respond to changing customer demand. The usual auto repair shops will no longer store a ton of spare parts in their warehouse — they will simply print the part you need on the spot.
3D printing technology allows you to create lighter, stronger and more complex structures cheaper than traditional methods of working with the material. For example, scientists from Livermore National Laboratory have learned to use 3D printing to make steel parts twice as strong as those produced by the traditional method. And last year, the startup Markforged released the first 3D printer worth less than a hundred thousand dollars. With the exception of the high cost, the technology may well be used by an ordinary consumer — for this it is not necessary to be an engineer and understand the intricacies of 3D printing. Desktop Metal company already offers a program that will make a ready-to-print model for the user. All that is required is to specify the characteristics of the item you need.
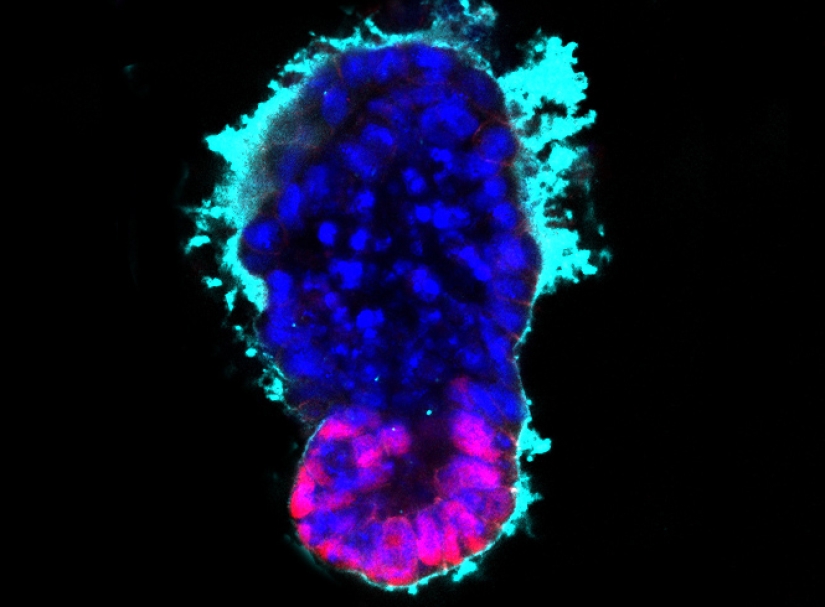
Artificial life
Scientists-embryologists from the University of Cambridge for the first time managed to grow a mouse embryo from stem cells alone — no sperm and egg. This breakthrough turns our idea of the creation of life upside down, because everything that is required for the birth of a living being can literally be taken with a pipette from another embryo.
The technology of using stem cells provides scientists with countless opportunities to study the problems associated with diseases that arise at the stage of fetal conception, and the possibility of studying the process of the birth of new organs — during the development of the embryo, one can observe how individual cells develop certain functions during growth - thus opening up the potential for the possible cultivation of artificial organs.
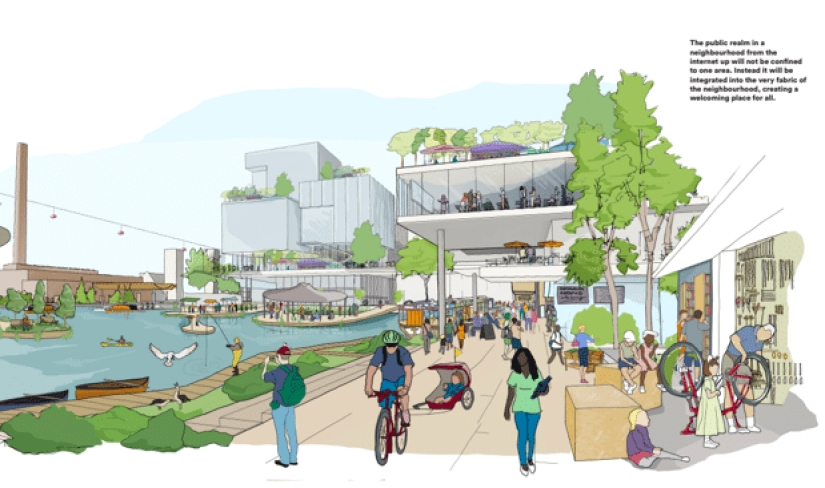

Smart cities
The integration of digital technologies and space planning can lead to a fundamentally new way of life in the cities of the future. Sensors and sensors that will flood cities will monitor pollution levels, noise and traffic density in real time and shift part of the troubleshooting tasks to automated programs and robots that will be able to take the necessary regulatory measures at such a speed that residents will never have to stand in traffic or write a noise complaint near a residential block again.
One of the most successful projects in this area is the Marina, which is being developed by Google's subsidiary Sidewalk Labs. The project provides for the introduction of an underground system of robot workers who will deliver parcels and goods and perform other work that loads urban infrastructure exclusively underground, which will free up roads and reduce pollution.
This automated system will be assisted by a widely implemented network of sensors that monitor a variety of data about the urban environment, including the activity of residents and businesses. Such a network will be able to identify patterns in activity, opening up opportunities for optimizing urban space. Residents will no longer have to worry about congested roads on their way to work, and a unified information network will allow you to check the congestion of popular places for recreation, such as parks or museums, before going there with your family. Despite this, the massive collection of data on the activity of residents greatly worries those who are not ready to share personal information — after all, in the case of, say, a hacker attack, this data can be used by attackers who can track where you are at any time and which route you most often return home.
Battles of neural networks
Artificial intelligence is getting better and better at tasks that may seem routine and do not cause us to associate with high technology — such as processing a lot of photos and determining which one shows a person and which one shows a giraffe. However, it is the ability to accurately distinguish and identify one or another object among an array of information that separates narrow-profile neural networks from truly working artificial intelligence.
Until today, progress in this area has been limited by the ability of the neural network to distinguish a conditional person from a giraffe and was characterized by a complete lack of creativity. Simply creating an image of a person remained an impossible task for neural networks - even after studying an array of data about how a person looks. The neural network, trying to create an image of a person on its own, would now and then draw an extra eyebrow on his forehead or a third hand.
The new method, first described by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, solves this problem by means of a competition between two neural networks — one of which acts as an idea generator, and the other as a discriminator. This division of labor into two neural networks provides quality control over the imagination of the "generator", which gradually learns from its mistakes, accepting comments from the discriminator, and over time begins to produce images indistinguishable from real objects — only completely fictional.
Progress in this technology means that soon computers will be able to create images that even a person cannot distinguish from real ones. Here, for example, are photos of fictional celebrities created by a computer.
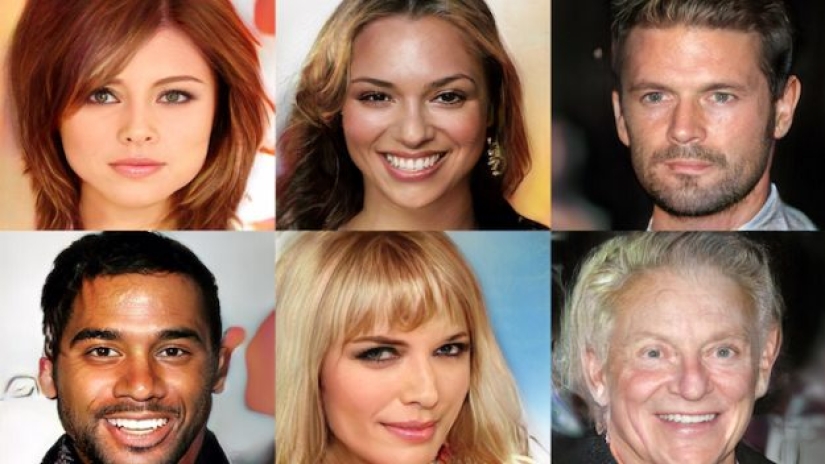

Researchers from Nvidia trained neural networks on photos of celebrities to create realistic images of people who do not exist. Many experts believe that the ability of neural networks to accurately distinguish objects reflects their growing ability to truly understand the world around them, and hence their rapid independence from human instructions.
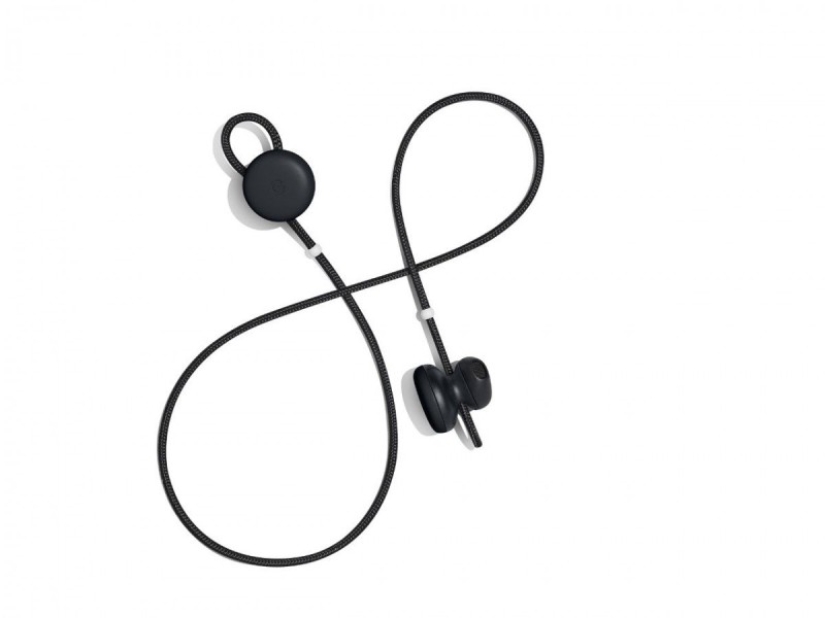

Headphones-translators
The technology, closely connected with neural networks, has made it possible to realize the long-standing fantasy of science fiction authors. Google recently released Pixel Buds - headphones, which many commentators called Babel-Fish Earbuds, referring to the popular science fiction book "Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy", in which the so-called Babel fish penetrated into the ear and allowed to understand foreign speech.

DNA Divination
Technology that predicts cancer risks or the likelihood of getting hooked on tobacco and reveals having an above-average IQ or a predisposition to music has recently become possible thanks to the processing of a huge array of DNA data from millions of people. Having conducted research and identified patterns in the behavior of certain types of genes, scientists can now create high-precision "passports" of disease risk, as well as passports of benign characteristics.
This can help researchers in the field of medicine and pharmaceuticals, significantly reducing the cost of false alarms and unnecessary examinations of patients whose genes - as it will now be possible to check — are not even conducive to the disease. Scientists conducting clinical trials in an attempt to find a cure for Alzheimer's disease will be able to more accurately select control groups of patients - thus increasing the effectiveness of research.
However, the fact that DNA reading technology can predict not only a disease, but any trait in general, puts ethical concerns at the forefront. How will parents and teachers use information about a child's predisposition to a particular subject? Will a person be able to raise a child knowing for sure that he will have cancer, and will he want to know himself what is the probability that he will develop Alzheimer's? Passports of risks and characteristics may also raise the issue of discrimination at work or when hiring. It is unprofitable for an employer to invest in professional development of an employee with a high risk of heart disease — therefore, with the spread of this technology, we have to think about the privacy of this data.
Keywords: 3D printer | Future | Invention | Scientists
Post News ArticleRecent articles

It's high time to admit that this whole hipster idea has gone too far. The concept has become so popular that even restaurants have ...

There is a perception that people only use 10% of their brain potential. But the heroes of our review, apparently, found a way to ...
Related articles

There is a perception that people only use 10% of their brain potential. But the heroes of our review, apparently, found a way to ...

The invention of flying machines that allow people to travel into the Earth's atmosphere is a list of the greatest innovations of ...

We all sometimes there are days when it is boring. The series is no longer pleasing, the weather "bad", all your friends are busy ...

New Year's is a time to surprise and delight loved ones not only with gifts but also with a unique presentation of the holiday ...